Welcome back, everyone. In this lecture, we’re going to discuss the built-in modules. That is the Python math module.
It’s essentially just a module that holds a ton of useful math functions. We won’t go through every single one, but we’ll show you how to find them. And then there’s the Python random module that contains a lot of mathematical random functions, as well as random functions for grabbing a random item from a python list.
But let’s explore these in more detail.
Python Math Modules
If you’re looking for a link to the documentation online, or you can just Google search math python module and you’ll first link will be the official documentation.
Let’s go ahead and start off with the math module going to import math.
import mathAnd if you want to figure out what’s available to you in math, you can actually just call help math.
help(math)Python Math Methods List
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| math.acos() | Returns the arc cosine of a number |
| math.acosh() | Returns the inverse hyperbolic cosine of a number |
| math.asin() | Returns the arc sine of a number |
| math.asinh() | Returns the inverse hyperbolic sine of a number |
| math.atan() | Returns the arc tangent of a number in radians |
| math.atan2() | Returns the arc tangent of y/x in radians |
| math.atanh() | Returns the inverse hyperbolic tangent of a number |
| math.ceil() | Rounds a number up to the nearest integer |
| math.comb() | Returns the number of ways to choose k items from n items without repetition and order |
| math.copysign() | Returns a float consisting of the value of the first parameter and the sign of the second parameter |
| math.cos() | Returns the cosine of a number |
| math.cosh() | Returns the hyperbolic cosine of a number |
| math.degrees() | Converts an angle from radians to degrees |
| math.dist() | Returns the Euclidean distance between two points (p and q), where p and q are the coordinates of that point |
| math.erf() | Returns the error function of a number |
| math.erfc() | Returns the complementary error function of a number |
| math.exp() | Returns E raised to the power of x |
| math.expm1() | Returns Ex – 1 |
| math.fabs() | Returns the absolute value of a number |
| math.factorial() | Returns the factorial of a number |
| math.floor() | Rounds a number down to the nearest integer |
| math.fmod() | Returns the remainder of x/y |
| math.frexp() | Returns the mantissa and the exponent, of a specified number |
| math.fsum() | Returns the sum of all items in any iterable (tuples, arrays, lists, etc.) |
| math.gamma() | Returns the gamma function at x |
| math.gcd() | Returns the greatest common divisor of two integers |
| math.hypot() | Returns the Euclidean norm |
| math.isclose() | Checks whether two values are close to each other, or not |
| math.isfinite() | Checks whether a number is finite or not |
| math.isinf() | Checks whether a number is infinite or not |
| math.isnan() | Checks whether a value is NaN (not a number) or not |
| math.isqrt() | Rounds a square root number downwards to the nearest integer |
| math.ldexp() | Returns the inverse of math.frexp() which is x * (2**i) of the given numbers x and i |
| math.lgamma() | Returns the log gamma value of x |
| math.log() | Returns the natural logarithm of a number, or the logarithm of number to base |
| math.log10() | Returns the base-10 logarithm of x |
| math.log1p() | Returns the natural logarithm of 1+x |
| math.log2() | Returns the base-2 logarithm of x |
| math.perm() | Returns the number of ways to choose k items from n items with order and without repetition |
| math.pow() | Returns the value of x to the power of y |
| math.prod() | Returns the product of all the elements in an iterable |
| math.radians() | Converts a degree value into radians |
| math.remainder() | Returns the closest value that can make numerator completely divisible by the denominator |
| math.sin() | Returns the sine of a number |
| math.sinh() | Returns the hyperbolic sine of a number |
| math.sqrt() | Returns the square root of a number |
| math.tan() | Returns the tangent of a number |
| math.tanh() | Returns the hyperbolic tangent of a number |
| math.trunc() | Returns the truncated integer parts of a number |
Lets some practical work, How to Round Numbers in Python math Module?
value =4.35
math.floor(value)
Output: 4math.floor() method is used to rounds a number DOWN to the nearest integer of the given value.
math.ceil(value)Output: 5math.ciel() method is used to rounds a number UP to the nearest integer of the given value.

Custom Base
The math. log() method is used to returns the natural logarithm value of a number or the logarithm of a number to base.
# math.log(x,base)
math.log(100,10)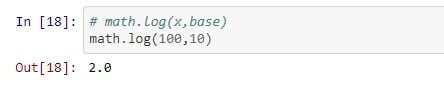
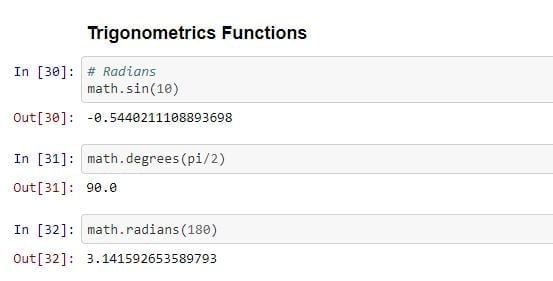
Trigonometric Functions
Python math module also have trigonometric functions like sin, cos, etc.
Mathematical Constants

Logarithmic Values

Must Read:
We have discussed in this article how to use the Python math Module, their types, how to work with practical examples, and snapshots. After this module, we will discuss the Python random Module.